Note
Click here to download the full example code
Compare two sorters¶
This example show how to compare the result of two sorters.
Import
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spikeinterface as si
import spikeinterface.extractors as se
import spikeinterface.sorters as ss
import spikeinterface.comparison as sc
import spikeinterface.widgets as sw
- First, let’s download a simulated dataset
from the repo ‘https://gin.g-node.org/NeuralEnsemble/ephy_testing_data’
local_path = si.download_dataset(remote_path='mearec/mearec_test_10s.h5')
recording, sorting = se.read_mearec(local_path)
print(recording)
print(sorting)
MEArecRecordingExtractor: 32 channels - 1 segments - 32.0kHz - 10.000s
file_path: /home/docs/spikeinterface_datasets/ephy_testing_data/mearec/mearec_test_10s.h5
MEArecSortingExtractor: 10 units - 1 segments - 32.0kHz
file_path: /home/docs/spikeinterface_datasets/ephy_testing_data/mearec/mearec_test_10s.h5
Then run two spike sorters and compare their output.
sorting_HS = ss.run_herdingspikes(recording)
sorting_TDC = ss.run_tridesclous(recording)
# Generating new position and neighbor files from data file
# Not Masking any Channels
# Sampling rate: 32000
# Localization On
# Number of recorded channels: 32
# Analysing frames: 320000; Seconds: 10.0
# Frames before spike in cutout: 10
# Frames after spike in cutout: 58
# tcuts: 42 90
# tInc: 100000
# Detection completed, time taken: 0:00:00.608594
# Time per frame: 0:00:00.001902
# Time per sample: 0:00:00.000059
Loaded 713 spikes.
Fitting dimensionality reduction using all spikes...
...projecting...
...done
Clustering...
Clustering 713 spikes...
number of seeds: 10
seeds/job: 6
using 2 cpus
[Parallel(n_jobs=2)]: Using backend LokyBackend with 2 concurrent workers.
[Parallel(n_jobs=2)]: Done 2 out of 2 | elapsed: 2.2s finished
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/spikeinterface/conda/0.95.0/lib/python3.8/site-packages/herdingspikes/clustering/mean_shift_.py:242: DeprecationWarning: `np.bool` is a deprecated alias for the builtin `bool`. To silence this warning, use `bool` by itself. Doing this will not modify any behavior and is safe. If you specifically wanted the numpy scalar type, use `np.bool_` here.
Deprecated in NumPy 1.20; for more details and guidance: https://numpy.org/devdocs/release/1.20.0-notes.html#deprecations
unique = np.ones(len(sorted_centers), dtype=np.bool)
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/spikeinterface/conda/0.95.0/lib/python3.8/site-packages/herdingspikes/clustering/mean_shift_.py:255: DeprecationWarning: `np.int` is a deprecated alias for the builtin `int`. To silence this warning, use `int` by itself. Doing this will not modify any behavior and is safe. When replacing `np.int`, you may wish to use e.g. `np.int64` or `np.int32` to specify the precision. If you wish to review your current use, check the release note link for additional information.
Deprecated in NumPy 1.20; for more details and guidance: https://numpy.org/devdocs/release/1.20.0-notes.html#deprecations
labels = np.zeros(n_samples, dtype=np.int)
Number of estimated units: 7
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/spikeinterface/conda/0.95.0/lib/python3.8/site-packages/tridesclous/dataio.py:175: DeprecationWarning: distutils Version classes are deprecated. Use packaging.version instead.
v1 = distutils.version.LooseVersion(tridesclous_version).version
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/spikeinterface/conda/0.95.0/lib/python3.8/site-packages/tridesclous/dataio.py:176: DeprecationWarning: distutils Version classes are deprecated. Use packaging.version instead.
v2 = distutils.version.LooseVersion(self.info['tridesclous_version']).version
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/spikeinterface/conda/0.95.0/lib/python3.8/site-packages/tridesclous/dataio.py:175: DeprecationWarning: distutils Version classes are deprecated. Use packaging.version instead.
v1 = distutils.version.LooseVersion(tridesclous_version).version
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/spikeinterface/conda/0.95.0/lib/python3.8/site-packages/tridesclous/dataio.py:176: DeprecationWarning: distutils Version classes are deprecated. Use packaging.version instead.
v2 = distutils.version.LooseVersion(self.info['tridesclous_version']).version
The compare_two_sorters() function allows us to compare the spike
sorting output. It returns a SymmetricSortingComparison object, with methods
to inspect the comparison output easily. The comparison matches the
units by comparing the agreement between unit spike trains.
Let’s see how to inspect and access this matching.
cmp_HS_TDC = sc.compare_two_sorters(
sorting1=sorting_HS,
sorting2=sorting_TDC,
sorting1_name='HS',
sorting2_name='TDC',
)
We can check the agreement matrix to inspect the matching.
sw.plot_agreement_matrix(cmp_HS_TDC)
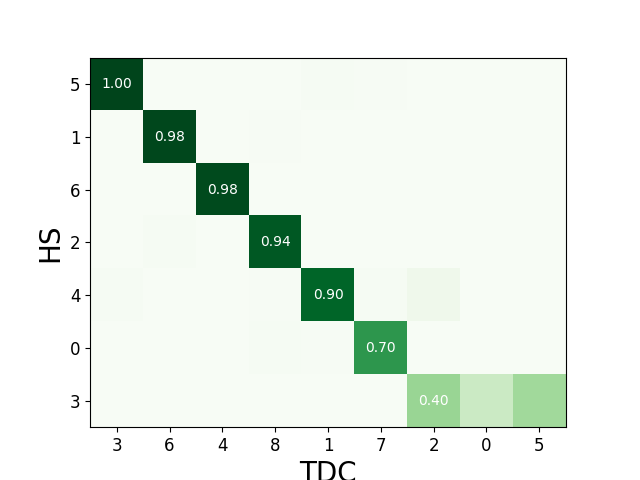
<spikeinterface.widgets._legacy_mpl_widgets.agreementmatrix.AgreementMatrixWidget object at 0x7f29952fd700>
Some useful internal dataframes help to check the match and count like match_event_count or agreement_scores
print(cmp_HS_TDC.match_event_count)
print(cmp_HS_TDC.agreement_scores)
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 162 3
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 127 1 1
2 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 1 104
3 30 0 51 0 0 48 0 0 0
4 0 53 6 1 0 0 0 2 1
5 0 1 0 50 0 0 0 1 0
6 0 0 0 0 42 0 0 0 0
0 1 2 ... 6 7 8
0 0.000000 0.004000 0.000000 ... 0.003067 0.704348 0.009836
1 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 ... 0.984496 0.003125 0.004237
2 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 ... 0.008621 0.003356 0.936937
3 0.232558 0.000000 0.395349 ... 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000
4 0.000000 0.898305 0.057692 ... 0.000000 0.007968 0.005952
5 0.000000 0.009804 0.000000 ... 0.000000 0.004115 0.000000
6 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 ... 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000
[7 rows x 9 columns]
In order to check which units were matched, the get_matching
methods can be used. If units are not matched they are listed as -1.
sc_to_tdc, tdc_to_sc = cmp_HS_TDC.get_matching()
print('matching HS to TDC')
print(sc_to_tdc)
print('matching TDC to HS')
print(tdc_to_sc)
matching HS to TDC
0 7.0
1 6.0
2 8.0
3 -1.0
4 1.0
5 3.0
6 4.0
dtype: float64
matching TDC to HS
0 -1.0
1 4.0
2 -1.0
3 5.0
4 6.0
5 -1.0
6 1.0
7 0.0
8 2.0
dtype: float64
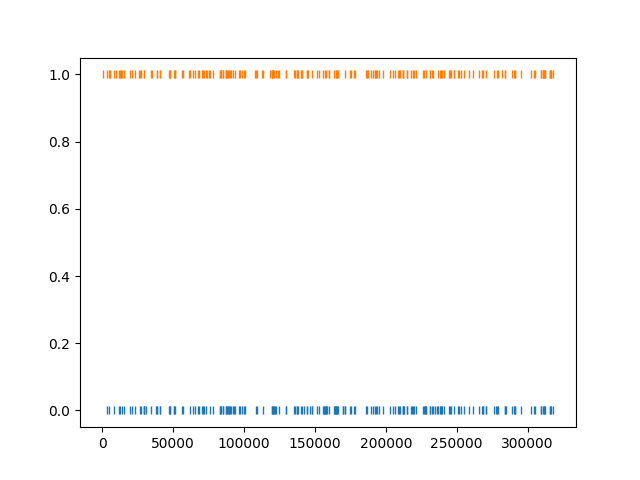
The get_unit_spike_train() returns the mapped spike train. We
can use
it to check the spike times.
matched_ids = sc_to_tdc[sc_to_tdc != -1]
unit_id_HS = matched_ids.index[0]
unit_id_TDC = matched_ids[unit_id_HS]
# check that matched spike trains correspond
st1 = sorting_HS.get_unit_spike_train(unit_id_HS)
st2 = sorting_TDC.get_unit_spike_train(unit_id_TDC)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(st1, np.zeros(st1.size), '|')
ax.plot(st2, np.ones(st2.size), '|')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 14.382 seconds)