Note
Click here to download the full example code
Compare multiple sorters and consensus based method¶
With 3 or more spike sorters, the comparison is implemented with a graph-based method. The multiple sorter comparison also allows to clean the output by applying a consensus-based method which only selects spike trains and spikes in agreement with multiple sorters.
Import
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import spikeinterface.extractors as se
import spikeinterface.sorters as ss
import spikeinterface.comparison as sc
import spikeinterface.widgets as sw
First, let’s create a toy example:
recording, sorting = se.example_datasets.toy_example(num_channels=4, duration=20, seed=0)
Then run 3 spike sorters and compare their output.
sorting_KL = ss.run_klusta(recording)
sorting_MS4 = ss.run_mountainsort4(recording)
sorting_TDC = ss.run_tridesclous(recording)
Out:
RUNNING SHELL SCRIPT: /home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/spikeinterface/checkouts/0.13.0/examples/modules/comparison/klusta_output/run_klusta.sh
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/spikeinterface/checkouts/0.13.0/doc/sources/spikesorters/spikesorters/basesorter.py:158: ResourceWarning: unclosed file <_io.TextIOWrapper name=63 encoding='UTF-8'>
self._run(recording, self.output_folders[i])
Warning! The recording is already filtered, but Mountainsort4 filter is enabled. You can disable filters by setting 'filter' parameter to False
{'chunksize': 3000,
'clean_cluster': {'apply_auto_merge_cluster': True,
'apply_auto_split': True,
'apply_trash_low_extremum': True,
'apply_trash_not_aligned': True,
'apply_trash_small_cluster': True},
'clean_peaks': {'alien_value_threshold': None, 'mode': 'extremum_amplitude'},
'cluster_kargs': {'adjacency_radius_um': 0.0,
'high_adjacency_radius_um': 0.0,
'max_loop': 1000,
'min_cluster_size': 20},
'cluster_method': 'pruningshears',
'duration': 20.0,
'extract_waveforms': {'wf_left_ms': -2.0, 'wf_right_ms': 3.0},
'feature_kargs': {'n_components': 8},
'feature_method': 'global_pca',
'make_catalogue': {'inter_sample_oversampling': False,
'sparse_thresh_level2': 3,
'subsample_ratio': 'auto'},
'memory_mode': 'memmap',
'mode': 'dense',
'n_jobs': -1,
'n_spike_for_centroid': 350,
'noise_snippet': {'nb_snippet': 300},
'peak_detector': {'adjacency_radius_um': 200.0,
'engine': 'numpy',
'method': 'global',
'peak_sign': '-',
'peak_span_ms': 0.7,
'relative_threshold': 5,
'smooth_radius_um': None},
'peak_sampler': {'mode': 'rand', 'nb_max': 20000, 'nb_max_by_channel': None},
'preprocessor': {'common_ref_removal': False,
'engine': 'numpy',
'highpass_freq': 400.0,
'lostfront_chunksize': -1,
'lowpass_freq': 5000.0,
'smooth_size': 0},
'sparse_threshold': 1.5}
Compare multiple spike sorter outputs¶
mcmp = sc.compare_multiple_sorters(sorting_list=[sorting_KL, sorting_MS4, sorting_TDC],
name_list=['KL', 'MS4', 'TDC'], verbose=True)
Out:
Multicomaprison step 1: pairwise comparison
Comparing: KL and MS4
Comparing: KL and TDC
Comparing: MS4 and TDC
Multicomaprison step 2: make graph
Multicomaprison step 3: clean graph
Removed 0 duplicate nodes
Multicomaprison step 4: extract agreement from graph
The multiple sorters comparison internally computes pairwise comparison, that can be accessed as follows:
print(mcmp.comparisons[0].sorting1, mcmp.comparisons[0].sorting2)
mcmp.comparisons[0].get_mapped_sorting1().get_mapped_unit_ids()
Out:
<spikeextractors.extractors.klustaextractors.klustaextractors.KlustaSortingExtractor object at 0x7f3dfc303a20> <spikeextractors.extractors.mdaextractors.mdaextractors.MdaSortingExtractor object at 0x7f3e05685fd0>
[6, 10, 3, 9, -1, -1, -1]
print(mcmp.comparisons[1].sorting1, mcmp.comparisons[1].sorting2)
mcmp.comparisons[0].get_mapped_sorting1().get_mapped_unit_ids()
Out:
<spikeextractors.extractors.klustaextractors.klustaextractors.KlustaSortingExtractor object at 0x7f3dfc303a20> <spikeextractors.extractors.tridescloussortingextractor.tridescloussortingextractor.TridesclousSortingExtractor object at 0x7f3dfc25f7f0>
[6, 10, 3, 9, -1, -1, -1]
The global multi comparison can be visualized with this graph
sw.plot_multicomp_graph(mcmp)
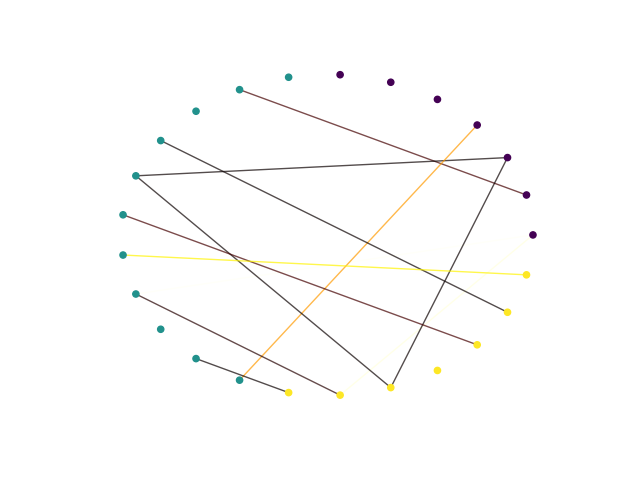
Out:
<spikewidgets.widgets.multicompgraphwidget.multicompgraphwidget.MultiCompGraphWidget object at 0x7f3dfc25f7b8>
We can see that there is a better agreement between tridesclous and mountainsort (5 units matched), while klusta only has two matched units with tridesclous, and three with mountainsort.
Consensus-based method¶
We can pull the units in agreement with different sorters using the
get_agreement_sorting method. This allows to make spike sorting more
robust by integrating the output of several algorithms. On the other
hand, it might suffer from weak performance of single algorithms.
When extracting the units in agreement, the spike trains are modified so that only the true positive spikes between the comparison with the best match are used.
agr_3 = mcmp.get_agreement_sorting(minimum_agreement_count=3)
print('Units in agreement for all three sorters: ', agr_3.get_unit_ids())
Out:
Units in agreement for all three sorters: [0, 2]
agr_2 = mcmp.get_agreement_sorting(minimum_agreement_count=2)
print('Units in agreement for at least two sorters: ', agr_2.get_unit_ids())
Out:
Units in agreement for at least two sorters: [0, 1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10, 12]
agr_all = mcmp.get_agreement_sorting()
The unit index of the different sorters can also be retrieved from the
agreement sorting object (agr_3) property sorter_unit_ids.
print(agr_3.get_shared_unit_property_names())
Out:
['agreement_number', 'avg_agreement', 'sorter_unit_ids']
print(agr_3.get_unit_ids())
# take one unit in agreement
u = agr_3.get_unit_ids()[0]
print(agr_3.get_unit_property(u, 'sorter_unit_ids'))
Out:
[0, 2]
{'MS4': 6, 'KL': 0, 'TDC': 1}
Now that we found our unit, we can plot a rasters with the spike trains of the single sorters and the one from the consensus based method. When extracting the agreement sorting, spike trains are cleaned so that only true positives remain from the comparison with the largest agreement are kept. Let’s take a look at the raster plots for the different sorters and the agreement sorter:
d = agr_3.get_unit_property(u, 'sorter_unit_ids')
st0 = sorting_KL.get_unit_spike_train(d['KL'])
st1 = sorting_MS4.get_unit_spike_train(d['MS4'])
st2 = sorting_TDC.get_unit_spike_train(d['TDC'])
st3 = agr_3.get_unit_spike_train(u)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(st0, 0 * np.ones(st0.size), '|')
ax.plot(st1, 1 * np.ones(st1.size), '|')
ax.plot(st2, 2 * np.ones(st2.size), '|')
ax.plot(st3, 3 * np.ones(st3.size), '|')
print('Klusta spike train length', st0.size)
print('Mountainsort spike train length', st1.size)
print('Tridesclous spike train length', st2.size)
print('Agreement spike train length', st3.size)
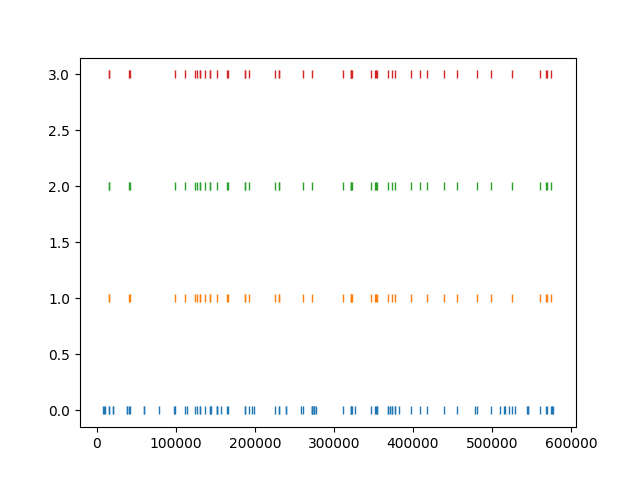
Out:
Klusta spike train length 93
Mountainsort spike train length 47
Tridesclous spike train length 48
Agreement spike train length 48
As we can see, the best match is between Mountainsort and Tridesclous, but only the true positive spikes make up the agreement spike train.
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 7.536 seconds)