Note
Click here to download the full example code
Preprocessing Tutorial¶
Before spike sorting, you may need to preproccess your signals in order to improve the spike sorting performance.
You can do that in SpikeInterface using the toolkit.preprocessing submodule.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
import scipy.signal
import spikeinterface.extractors as se
import spikeinterface.toolkit as st
First, let’s create a toy example:
recording, sorting = se.toy_example(num_channels=4, duration=10, seed=0)
Apply filters¶
Now apply a bandpass filter and a notch filter (separately) to the recording extractor. Filters are also RecordingExtractor objects. Note that theses operation are lazy the computation is done on the fly with rec.get_traces()
recording_bp = st.preprocessing.bandpass_filter(recording, freq_min=300, freq_max=6000)
print(recording_bp)
recording_notch = st.preprocessing.notch_filter(recording, freq=2000, q=30)
print(recording_notch)
Out:
BandpassFilterRecording: 4 channels - 2 segments - 30.0kHz - 20.000s
NotchFilterRecording: 4 channels - 2 segments - 30.0kHz - 20.000s
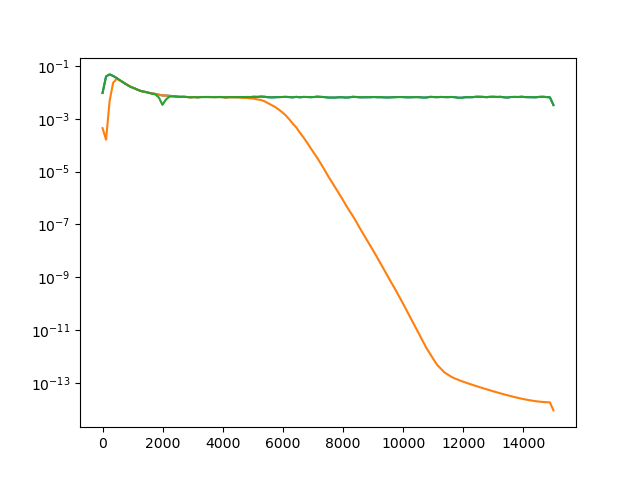
Now let’s plot the power spectrum of non-filtered, bandpass filtered, and notch filtered recordings.
fs = recording.get_sampling_frequency()
f_raw, p_raw = scipy.signal.welch(recording.get_traces(segment_index=0)[:, 0], fs=fs)
f_bp, p_bp = scipy.signal.welch(recording_bp.get_traces(segment_index=0)[:, 0], fs=fs)
f_notch, p_notch = scipy.signal.welch(recording_notch.get_traces(segment_index=0)[:, 0], fs=fs)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.semilogy(f_raw, p_raw, f_bp, p_bp, f_notch, p_notch)
Out:
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7f0158cdfac0>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7f0158cdf0a0>, <matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7f0158cdf700>]
Compute LFP and MUA¶
Local field potentials (LFP) are low frequency components of the extracellular recordings. Multi-unit activity (MUA) are rectified and low-pass filtered recordings showing the diffuse spiking activity.
In spiketoolkit, LFP and MUA can be extracted combining the
bandpass_filter, rectify and resample functions. In this
example LFP and MUA are resampled at 1000 Hz.
recording_lfp = st.preprocessing.bandpass_filter(recording, freq_min=1, freq_max=300)
# TODO alessio, this is for you
# recording_lfp = st.preprocessing.resample(recording_lfp, 1000)
# recording_mua = st.preprocessing.resample(st.preprocessing.rectify(recording), 1000)
The toy example data are only contain high frequency components, but these lines of code will work on experimental data
Change reference¶
In many cases, before spike sorting, it is wise to re-reference the signals to reduce the common-mode noise from the recordings.
To re-reference in spiketoolkit you can use the common_reference
function. Both common average reference (CAR) and common median
reference (CMR) can be applied. Moreover, the average/median can be
computed on different groups. Single channels can also be used as
reference.
recording_car = st.common_reference(recording, reference='global', operator='average')
recording_cmr = st.common_reference(recording, reference='global', operator='median')
recording_single = st.common_reference(recording, reference='single', ref_channels=[1])
recording_single_groups = st.common_reference(recording, reference='single',
groups=[[0, 1], [2, 3]], ref_channels=[0, 2])
trace0_car = recording_car.get_traces(segment_index=0)[:, 0]
trace0_cmr = recording_cmr.get_traces(segment_index=0)[:, 0]
trace0_single = recording_single.get_traces(segment_index=0)[:, 0]
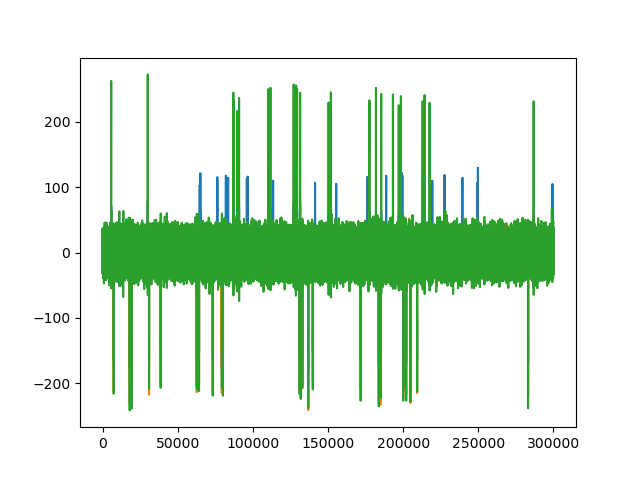
fig1, ax1 = plt.subplots()
ax1.plot(trace0_car)
ax1.plot(trace0_cmr)
ax1.plot(trace0_single)
trace1_groups = recording_single_groups.get_traces(segment_index=0)[:, 1]
trace0_groups = recording_single_groups.get_traces(segment_index=0)[:, 0]
fig2, ax2 = plt.subplots()
ax2.plot(trace1_groups) # not zero
ax2.plot(trace0_groups)
Out:
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7f01504c6d30>]
Remove stimulation artifacts¶
In some applications, electrodes are used to electrically stimulate the
tissue, generating a large artifact. In spiketoolkit, the artifact
can be zeroed-out using the remove_artifact function.
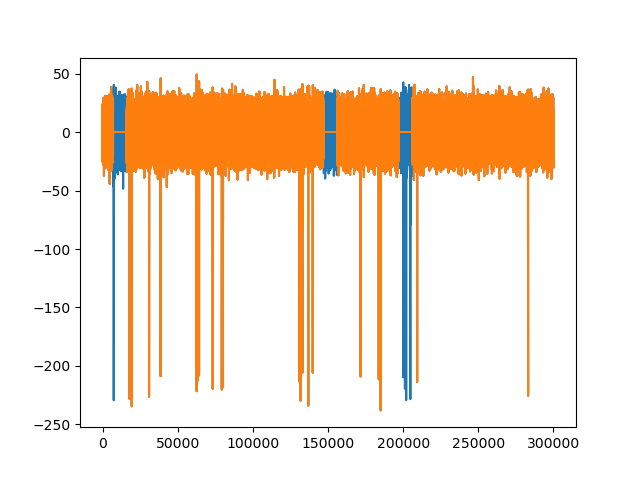
# create dummy stimulation triggers per segment
stimulation_trigger_frames = [
[10000, 150000, 200000],
[20000, 30000],
]
# large ms_before and s_after are used for plotting only
recording_rm_artifact = st.remove_artifacts(recording, stimulation_trigger_frames,
ms_before=100, ms_after=200)
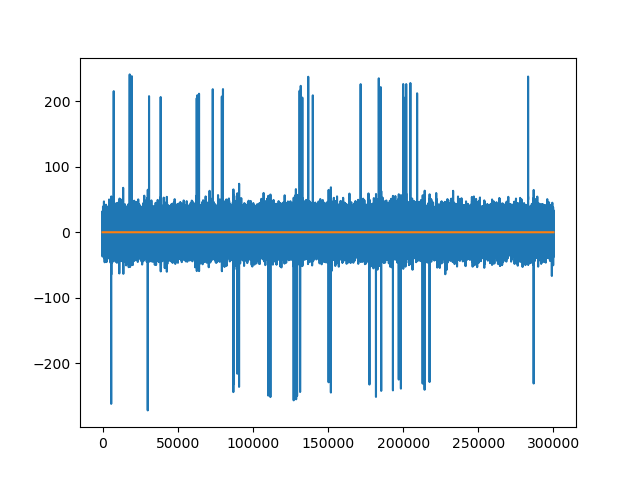
trace0 = recording.get_traces(segment_index=0)[:, 0]
trace0_rm = recording_rm_artifact.get_traces(segment_index=0)[:, 0]
fig3, ax3 = plt.subplots()
ax3.plot(trace0)
ax3.plot(trace0_rm)
Out:
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7f0158f1b250>]
You can list the available preprocessors with:
from pprint import pprint
pprint(st.preprocesser_dict)
plt.show()
Out:
{'bandpass_filter': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.filter.BandpassFilterRecording'>,
'blank_staturation': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.clip.BlankSaturationRecording'>,
'center': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.normalize_scale.CenterRecording'>,
'common_reference': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.common_reference.CommonReferenceRecording'>,
'filter': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.filter.FilterRecording'>,
'normalize_by_quantile': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.normalize_scale.NormalizeByQuantileRecording'>,
'notch_filter': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.filter.NotchFilterRecording'>,
'rectify': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.rectify.RectifyRecording'>,
'remove_artifacts': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.remove_artifacts.RemoveArtifactsRecording'>,
'remove_bad_channels': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.remove_bad_channels.RemoveBadChannelsRecording'>,
'scale': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.normalize_scale.ScaleRecording'>,
'whiten': <class 'spikeinterface.toolkit.preprocessing.whiten.WhitenRecording'>}
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 2.132 seconds)